Imagine a world where the lights flicker and die, factories grind to a halt, and water treatment plants cease operation. This isn’t a dystopian fantasy; it’s the potential reality if we fail to secure Operational Technology (OT).
OT, the hardware and software that controls critical infrastructure and industrial processes, is increasingly connected to the internet, creating vulnerabilities ripe for exploitation. Once isolated, these systems are now targets for cyberattacks, with potentially devastating consequences ranging from economic disruption to environmental disasters and even loss of life.
This article delves into the critical world of OT cybersecurity, exploring the unique challenges involved in protecting these vital systems. We’ll uncover the common threats, discuss best practices for building a robust OT security posture, and examine the evolving landscape of regulations and technologies designed to keep our critical infrastructure safe and secure.
Prepare to learn how to safeguard the systems that underpin our modern world.
OT Cybersecurity: Protecting the Industrial Backbone
Operational Technology (OT) forms the very core of how our infrastructure and manufacturing processes work. From power plants to factories, these systems keep society moving. However, this crucial infrastructure is increasingly vulnerable to digital threats.
Cyberattacks on OT systems aren’t just theoretical; they’re happening. These attacks can disrupt operations, damage equipment, and even endanger lives. The need for robust OT cybersecurity measures has never been greater.
This article explores the key aspects of OT cybersecurity, the challenges it presents, and what organizations can do to defend themselves. We’ll cover everything from risk assessments to incident response.
Understanding the Unique Challenges of OT Cybersecurity
OT systems weren’t initially designed with cybersecurity in mind. Many legacy systems run on outdated software with known vulnerabilities, creating easy entry points for attackers. This poses a significant issue.
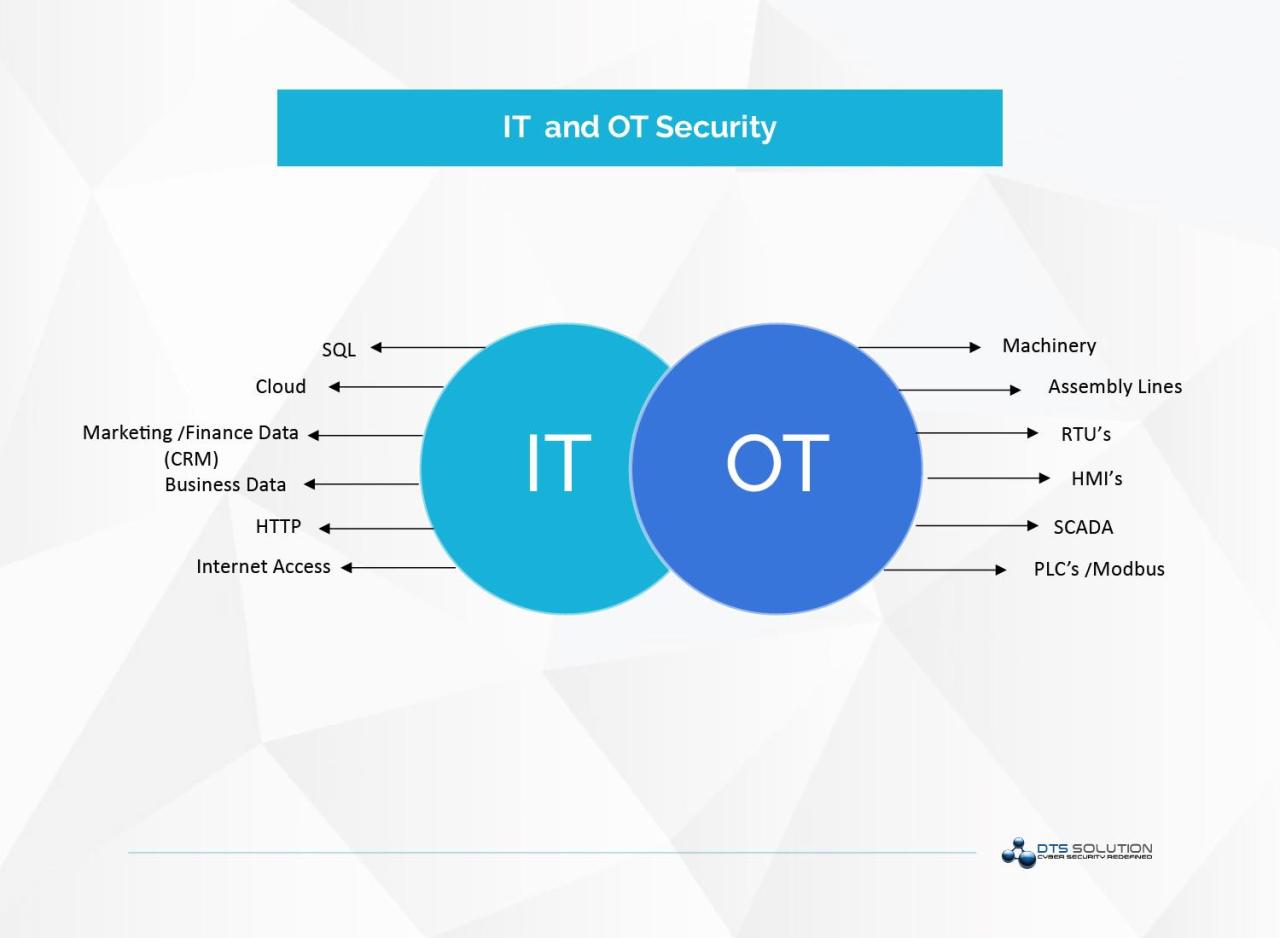
Unlike IT environments that prioritize confidentiality and integrity, OT environments often prioritize availability. Shutting down a critical system for patching may not be feasible, requiring alternative security strategies.
OT environments are often complex and heterogeneous, comprising a mix of different vendors, protocols, and technologies. This complexity makes it difficult to implement and maintain consistent security policies.
Another challenge lies in the limited visibility into OT network traffic. Traditional IT security tools may not be compatible with OT protocols, leaving security teams blind to potential threats. This creates a blindspot for defenders.
Key Components of an Effective OT Cybersecurity Strategy
A comprehensive OT cybersecurity strategy starts with a thorough risk assessment. Identify critical assets, vulnerabilities, and potential attack vectors. This helps prioritize security efforts and resources.
Network segmentation is vital to contain the impact of a potential breach. Isolating critical OT systems from the corporate IT network reduces the attack surface. This limits the damage a cyberattack can do.
Implementing strong authentication and access control measures is crucial to prevent unauthorized access to OT systems. Multifactor authentication adds an extra layer of protection. Only authorized users should have access.
Regular security monitoring and threat detection are essential for identifying and responding to cyberattacks in real time. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems can help analyze security logs.
Implementing Best Practices for OT Cybersecurity
Patching OT systems is essential, but it must be done carefully. Test patches in a non-production environment before deploying them to live systems. This prevents unintended downtime.
Develop and implement a robust incident response plan that outlines the steps to be taken in the event of a cyberattack. Practice the plan regularly through tabletop exercises. This ensures a swift response.
Provide regular cybersecurity training to OT personnel. Educate them about common threats, phishing scams, and best practices for secure operation. This helps prevent user errors.
Establish and maintain strong relationships with OT vendors. They can provide valuable insights into security vulnerabilities and best practices for their specific systems. Collaboration is key.
The Future of OT Cybersecurity
As OT systems become increasingly connected to the internet, the threat landscape will continue to evolve. Organizations must stay ahead of the curve by adopting new security technologies and strategies.
Cloud-based security solutions are gaining popularity in OT environments. These solutions offer scalable and cost-effective ways to improve security posture. They provide enhanced visibility and analytics.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are being used to automate threat detection and response in OT environments. These technologies can help security teams identify and address threats more quickly and effectively.
Collaboration between IT and OT security teams is becoming increasingly important. By breaking down silos and sharing knowledge, organizations can create a more unified and effective cybersecurity posture. A unified approach is essential.