Imagine managing your entire data center infrastructure with just a few clicks. Sounds appealing, doesn’t it? In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, businesses are constantly seeking ways to simplify IT operations, reduce costs, and improve agility. Enter hyperconverged servers, a revolutionary approach that’s rapidly transforming data centers.
But what exactly are they, and why should you care? Hyperconverged servers integrate compute, storage, networking, and virtualization resources into a single, software-defined system, drastically simplifying management and scaling. This article will delve into the core benefits of hyperconverged servers, exploring how they can streamline your IT environment, boost performance, and provide a more cost-effective solution compared to traditional infrastructure.
Get ready to discover how hyperconvergence can empower your business to thrive in the modern era.
Understanding Hyperconverged Servers: A Deep Dive
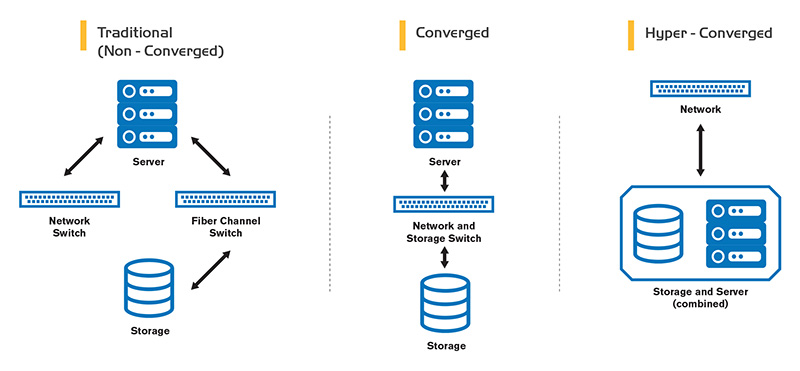
So, what exactly are hyperconverged servers? Picture this: all the essential parts of a data center—computing power, storage, and networking—bundled into one neat package. It’s a simplified approach to managing your IT infrastructure.
Think of it as a Lego set for your data center. Instead of wrestling with separate servers, storage arrays, and networking devices, you get pre-integrated blocks. These blocks work together smoothly, making deployment and management much easier.
Hyperconvergence isn’t just about convenience. It’s also about efficiency. By consolidating resources, it reduces the footprint of your data center and lowers operational costs.
Furthermore, these systems offer excellent scalability. As your business grows, you can easily add more blocks to increase capacity and performance. This modularity is a key advantage over traditional infrastructure.
The Core Components of Hyperconvergence
At its heart, hyperconvergence relies on virtualized computing. Each server node runs a hypervisor, which allows multiple virtual machines (VMs) to share the same physical resources. This virtualization is the foundation of its flexibility.
Storage is another crucial component. Hyperconverged systems use software-defined storage (SDS) to pool storage resources across multiple nodes. This eliminates the need for dedicated storage arrays and simplifies management.
Networking is also handled in software. Virtual switches and routers provide connectivity between VMs and external networks. This software-defined approach allows for greater agility and control over network traffic.
These components are managed through a central management interface. This interface provides a single pane of glass for monitoring and controlling the entire infrastructure. It greatly reduces the complexity of managing a data center.
Beyond the core components, you’ll often find features like data deduplication, compression, and replication. These features enhance efficiency and protect data against loss. They provide an additional layer of robustness.
Benefits of Switching to Hyperconverged Infrastructure
One of the biggest perks is simplified management. With everything integrated and managed through a single interface, IT teams can spend less time on routine tasks and more time on strategic initiatives.
The reduced footprint of hyperconverged systems translates into significant cost savings. Lower power consumption, less cooling, and reduced space requirements all contribute to a lower total cost of ownership.
Hyperconverged infrastructure offers excellent scalability. You can easily add more nodes to increase capacity and performance as your business grows. This scalability ensures that your infrastructure can keep pace with your evolving needs.
Improved data protection is another key benefit. Built-in features like data deduplication, replication, and backup ensure that your data is safe and readily available in case of a disaster. This promotes business continuity.
Faster deployment is also a significant advantage. Pre-integrated systems can be deployed much faster than traditional infrastructure. This speed allows you to get new applications and services up and running quickly.
Use Cases for Hyperconverged Servers
Virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) is a perfect use case. Hyperconvergence provides the performance and scalability needed to deliver a consistent user experience for virtual desktops. This ensures smooth application performance.
Disaster recovery is another strong application. Hyperconverged systems can be easily replicated to a remote site, providing a cost-effective solution for business continuity. Recovery is faster and more reliable.
Edge computing benefits greatly from hyperconvergence. The compact form factor and ease of management make it ideal for deploying IT infrastructure in remote locations. This is crucial for IoT and other edge applications.
General-purpose virtualization is a common use case. Hyperconvergence provides a flexible and scalable platform for running a wide range of virtualized workloads. This makes it suitable for various business needs.
Private cloud deployments are also well-suited for hyperconverged infrastructure. It provides the building blocks for creating a self-service IT environment. This gives organizations more control over their resources.
Choosing the Right Hyperconverged Solution
Consider your specific workload requirements. Some solutions are better suited for certain applications than others. Understand your performance and capacity needs before making a decision.
Evaluate the management capabilities of different solutions. A user-friendly interface and comprehensive monitoring tools are essential. This ensures ease of use and efficient management.
Think about the scalability of the solution. Ensure that it can easily accommodate your future growth. Choose a solution that can scale both vertically and horizontally.
Check the vendor’s support and services. Reliable support is crucial for resolving any issues that may arise. A good vendor will provide comprehensive documentation and training.
Finally, compare the total cost of ownership. Consider not only the upfront cost but also the ongoing operational expenses. This will give you a clearer picture of the overall value.