Imagine managing your entire data center infrastructure – compute, storage, networking – as a single, cohesive unit. Sound like a futuristic fantasy? It’s not. The increasing demands of modern businesses are pushing traditional IT infrastructures to their breaking point, leading to complexity, escalating costs, and stifled innovation.
Enter hyperconverged infrastructure, or HCI. Think of it as a revolutionary way to simplify IT by consolidating all the essential data center elements into a single, software-defined system. This article will explore how HCI streamlines operations, boosts agility, and unlocks significant cost savings.
We’ll delve into the core components of HCI, uncover the key benefits, and examine the common use cases where this technology is making a real impact. Get ready to discover how hyperconverged infrastructure can transform your IT landscape and propel your business forward.
Hyperconverged Infrastructure (HCI): What’s the Buzz About?
Hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) is changing how businesses view and manage their IT resources. It’s more than just a trend; it’s a fundamental shift in data center architecture.
It combines computing, storage, and networking into a single, integrated system. Forget complex, disparate hardware components; HCI offers simplicity.
Think of HCI as a unified platform, easier to manage than traditional setups. This makes it appealing to businesses seeking agility and simplified operations.
HCI solutions aim to streamline IT management, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency. This is done through software-defined management and automation.
One of the attractive things about HCI is its scalability. Easily add resources to scale the infrastructure as business needs evolve and grow.
The Core Components of Hyperconverged Systems
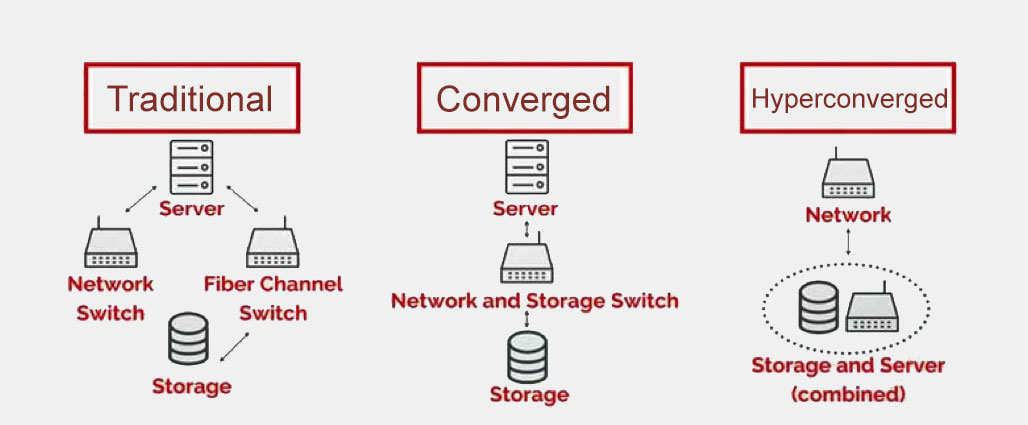
The essence of HCI lies in its integrated components. These work together to deliver a robust and efficient infrastructure solution. Let’s break down the key elements.
Compute: Virtualized servers handle processing power. This removes dependence on dedicated hardware servers to scale computer resources.
Storage: Software-defined storage pools resources across the cluster. It provides flexibility, efficiency, and optimizes resource allocation.
Networking: Virtualized networking simplifies network management. It enables faster deployment and streamlined operations using networking tools.
Virtualization: A hypervisor, like VMware vSphere or Nutanix AHV, is a must. It manages virtual machines (VMs) and resource allocation.
Management: Centralized management tools are very useful. They provide a single pane of glass for monitoring and controlling the entire infrastructure.
Benefits of Embracing Hyperconvergence
HCI offers a range of benefits that address common IT challenges. These advantages make it a compelling choice for many organizations. Here’s why it matters.
Simplified Management: Consolidating resources streamlines administration. Spend less time on day-to-day tasks using a centralized dashboard.
Scalability: Scale resources easily as your business grows. Add compute, storage, and networking capacity without complex reconfigurations.
Reduced Costs: Lower capital expenditures (CAPEX) and operational expenditures (OPEX). Reduce hardware footprint and management overhead to save money.
Improved Performance: Optimized resource utilization leads to faster performance. Applications run efficiently with software-defined control and orchestration.
Increased Agility: Deploy resources and applications more quickly. Respond to changing business needs with increased speed and responsiveness.
Use Cases for Hyperconverged Infrastructure
HCI’s versatility makes it suitable for different IT environments. Here are some typical scenarios where HCI shines. Consider these situations.
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI): Deliver virtual desktops efficiently. HCI handles the storage and processing demands of VDI deployments with ease.
Remote Office/Branch Office (ROBO): Standardize infrastructure across distributed locations. Simplify management and reduce hardware costs using integrated HCI.
Disaster Recovery (DR): Create a resilient DR environment. HCI can easily replicate data for rapid recovery in the event of a disaster.
Private Cloud: Build a private cloud infrastructure with self-service capabilities. HCI makes it easy to provision and manage virtual resources.
Business-Critical Applications: Run demanding applications with improved availability. HCI provides the performance and resilience these apps require.
Considerations Before Implementing HCI
Before jumping into HCI, consider several key factors. These insights help ensure a successful transition. Here are the details you need.
Workload Analysis: Understand your workload requirements. Determine the right HCI solution to meet your specific needs for data and bandwidth.
Vendor Selection: Choose a reputable HCI vendor. Evaluate factors like support, features, and integration capabilities before committing.
Network Requirements: Ensure your network can handle the increased traffic. HCI can generate higher network loads, so plan accordingly.
Skills and Training: Train your team on HCI management and maintenance. Staff must be ready to handle the new infrastructure efficiently.
Integration with Existing Infrastructure: Plan for smooth integration with existing systems. Compatibility is crucial for a successful transition.