In today’s data-driven world, is your organization truly leveraging its most valuable asset, or is it drowning in a sea of ungoverned information? The truth is, many businesses struggle to effectively manage and utilize their data, leading to missed opportunities, compliance risks, and inefficient operations.
This is where the Gartner Magic Quadrant for Data Governance steps in as a crucial guide. It offers a comprehensive evaluation of leading data governance solution providers, helping organizations navigate the complex landscape and identify the right tools to establish robust data governance frameworks.
Think of it as a compass in the wild west of data management, pointing towards solutions that can ensure data quality, compliance, and ultimately, better decision-making. In this article, we will delve into the significance of the Gartner Magic Quadrant for Data Governance, exploring its key components, highlighting notable vendors, and providing insights into how you can leverage this resource to enhance your organization’s data governance strategy and unlock the true potential of your data.
Decoding the Gartner Magic Quadrant for Data Governance Solutions
The Gartner Magic Quadrant is a respected research report. It visually represents the positioning of technology vendors. It focuses on specific markets, like data governance. It’s based on their completeness of vision and ability to execute.
For organizations seeking data governance tools, the Magic Quadrant serves as a handy compass. It shows the leading players. It gives insights into their strengths and weaknesses. This helps informed decision-making.
Understanding the Magic Quadrant is crucial. It helps you navigate the complexities of the vendor landscape. It makes sure you pick a data governance solution that aligns. It aligns with your business needs and goals.
This analysis provides a breakdown of the Gartner Magic Quadrant for Data Governance. It explains what it means. It will help you use it to make smart choices. It will assist your data governance strategy.
Understanding Data Governance and its Significance
Data governance is much more than just a buzzword. It’s a structured approach. It ensures data is managed effectively. This involves availability, usability, integrity, and security.
Effective data governance is vital. It drives better decisions. It promotes regulatory compliance. It enhances operational efficiency. It allows businesses to fully realize the value of their information.
Without data governance, organizations face risks. They risk data silos, inconsistencies, and inaccuracies. This can lead to poor business outcomes. They can even incur financial penalties.
Therefore, implementing data governance is a necessity. It is for any organization wanting to unlock the potential of its data. They must also minimize risks and ensure data quality.
Key Components Evaluated in the Magic Quadrant
Gartner evaluates vendors on two primary axes. They are “Completeness of Vision” and “Ability to Execute.” The Completeness of Vision assesses the vendor’s understanding of market trends. It also looks at their product strategy.
The Ability to Execute examines the vendor’s ability to deliver. It also looks at their sales and marketing effectiveness. Customer experience is also a factor, as is overall viability.
Based on these evaluations, vendors are placed into four quadrants. These are Leaders, Challengers, Visionaries, and Niche Players. Each quadrant represents a different position in the market.
Leaders demonstrate a strong vision. They also execute it well. Challengers have a strong ability to execute. However, their vision may be less comprehensive. Visionaries have a compelling vision. They may struggle with execution. Niche Players focus on specific segments.
They may have limited overall capabilities.
Decoding the Quadrants: Leaders, Challengers, Visionaries, and Niche Players
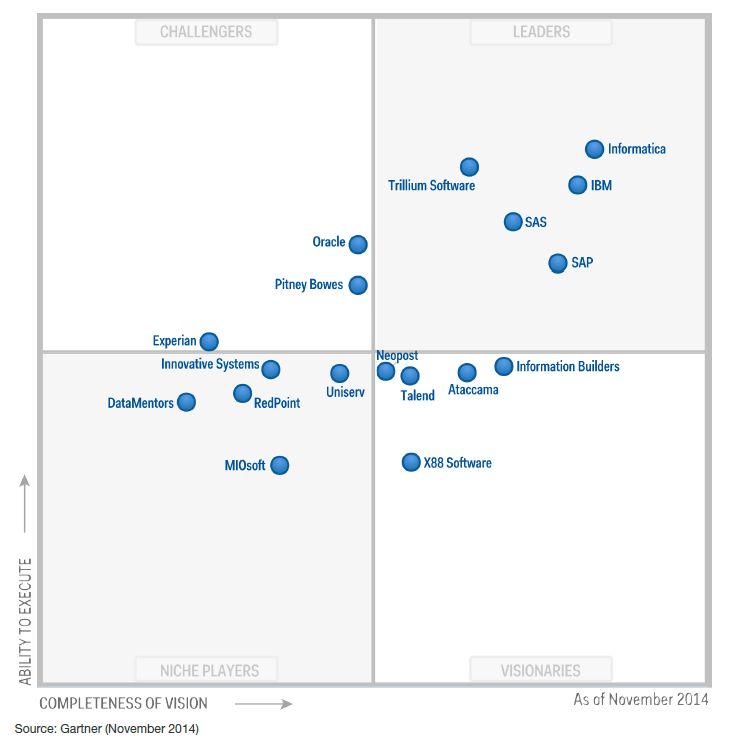
Leaders show a strong market understanding. They have a clear direction for their product. They also execute well. They’re typically larger companies with established solutions. They have a proven track record of success.
Challengers perform well currently. They may lack the innovation or vision. They may need to become market leaders. They are often focused on refining their existing offerings.
Visionaries understand how the market will change. They may be smaller or newer companies. They are focused on innovation. They may lack the resources for complete execution.
Niche Players focus on specific needs. They may have expertise in a particular industry. They may not have broad capabilities. They can be a good fit for specific needs.
How to Use the Magic Quadrant for Vendor Selection
The Magic Quadrant is a great starting point. It gives you a list of potential vendors to consider. Do not treat it as the only deciding factor. Think about your own specific needs. Consider your environment.
Consider your organization’s size and maturity. A large enterprise might prefer a Leader. A smaller business with unique needs might choose a Niche Player. Assess your budget and your resources.
Always conduct your due diligence. Request demos. Speak to existing customers. Test the solutions. Ensure the vendor’s roadmap aligns with your long-term data governance strategy.
Remember, the best solution is the one that fits your specific requirements. The Magic Quadrant is a helpful tool. It should be used with a thorough understanding of your own needs.