In today’s interconnected world, a chilling statistic echoes louder than ever: a cyberattack occurs every 39 seconds. That’s a stark reminder of the persistent and evolving threats lurking in the digital shadows, targeting everything from personal data to critical infrastructure.
But what shields organizations and individuals from becoming the next victim? The answer lies in a robust cybersecurity program. Think of it as your digital fortress, a comprehensive and proactive strategy encompassing policies, technologies, and training designed to protect your valuable assets from malicious actors.
This article will delve into the core elements of a successful cybersecurity program, exploring the common pitfalls to avoid and offering practical strategies to fortify your defenses. Whether you’re a seasoned IT professional or simply seeking to better protect your online presence, understanding the fundamentals of a well-structured cybersecurity program is no longer optional; it’s an absolute necessity.
Prepare to unlock the secrets to building a resilient and adaptable defense against the ever-present cyber threats.
Crafting a Rock-Solid Cybersecurity Program
Embarking on a cybersecurity program can feel daunting, a bit like navigating a complex maze. But fear not! Building a reliable defense doesn’t require superhuman effort; it’s about method, strategy, and consistent execution.
A robust program shields your assets, keeps data secure, and helps maintain trust. It’s no longer optional; it’s a cornerstone for survival in today’s digital world. Think of it as insurance for your business reputation.
This guide provides a practical roadmap. It outlines the essential steps, offering clear and understandable advice. Let’s delve into the essentials and start constructing your digital fortress.
Ready to safeguard your organization’s future? Let’s uncover the elements you need to assemble a formidable cybersecurity program. It’s about preparation and proactive measures.
Understanding Your Assets and Risks
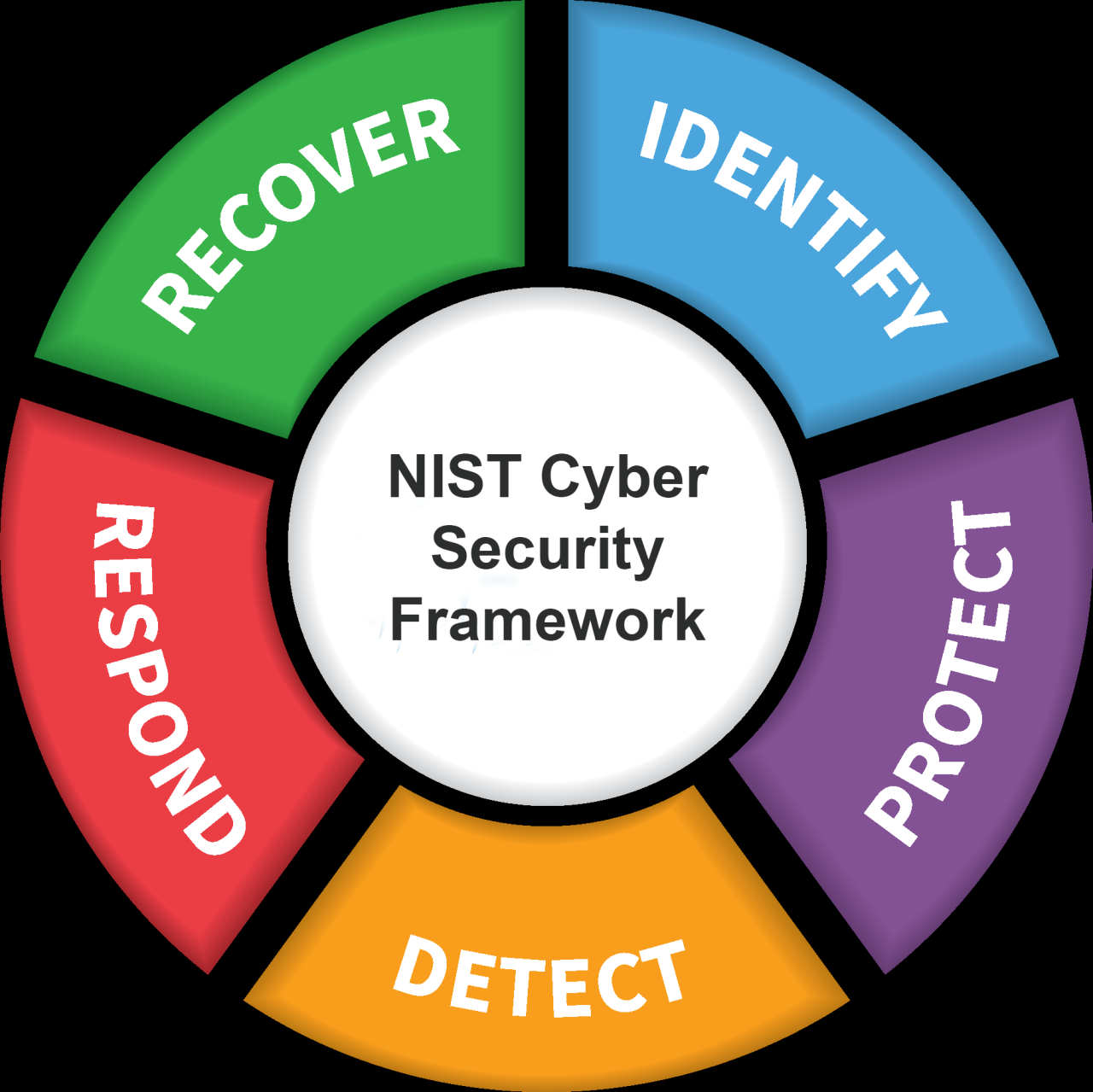
Before fortifying anything, you must know what to protect. Identify your key assets, such as sensitive data, critical systems, and intellectual property. Think servers, employee accounts, even physical hardware.
Next, analyze the risks those assets face. Consider everything: malware, phishing, data breaches, insider threats, and even physical vulnerabilities. A realistic assessment is absolutely crucial.
Map out potential entry points hackers could exploit. Determine the likelihood and impact of each threat. Prioritize resources based on what poses the biggest danger to your business.
Risk assessments should be continuous, not a one-time task. Reassess regularly as your business evolves and the threat landscape shifts. Stay vigilant to maintain effective defenses.
Use a vulnerability scanner to automatically find flaws in your infrastructure. This proactive approach can identify weaknesses before attackers do, strengthening your overall posture.
Developing Security Policies and Procedures
Security policies are the bedrock of your program. They outline rules and standards for acceptable behavior. For example, password guidelines, data access rules, and email usage protocol.
Procedures are the step-by-step instructions for putting those policies into practice. These are detailed how-to guides for everyday tasks. Incident response, onboarding, and software installation are all crucial.
Document everything clearly and simply. Anyone in the organization needs to understand and follow these guidelines. Confusing instructions will only lead to errors and vulnerabilities.
Policies and procedures should be living documents. Update them regularly to reflect changes in technology, regulations, and the threat landscape. Staying current is key to relevance.
Regular training on these policies and procedures is crucial. Ensure employees know their roles and responsibilities. Simulated phishing exercises can test their understanding in a realistic environment.
Implementing Security Controls and Technologies
Security controls are the safeguards you implement to mitigate risks. Think firewalls, intrusion detection systems, antivirus software, and access control mechanisms. This is your first line of defense.
Technology plays a vital part, but it’s not the whole story. People and processes are just as important. A balanced approach ensures comprehensive security that isn’t solely dependent on technology.
Choose technologies suited to your specific needs and risk profile. A small business will have different needs than a large enterprise. Avoid overkill; find solutions that scale appropriately.
Ensure your systems are properly configured and maintained. Regular patching, updates, and monitoring are essential. An unpatched server is an open invitation for attackers.
Regular security audits should review the effectiveness of your security controls. Pen tests can help to identify weaknesses in the architecture. Audits are vital for discovering hidden risks.
Training and Awareness Programs
Your employees are your first line of defense (and potentially your biggest weakness). Training and awareness programs are essential to equipping them to handle cyber threats. Make them cyber aware.
Cover topics such as phishing, social engineering, password security, and safe browsing habits. Make the training relevant to their roles and responsibilities. Use real-world examples to grab their interest.
Make security awareness a continuous process, not a one-time event. Regular reminders, updates, and simulations help reinforce good habits. Consistency cultivates a security-conscious culture.
Encourage employees to report suspicious activity. Create a culture of open communication. Make it easy for people to report concerns without fear of reprisal. Open reporting is the key.
Consider gamification or incentives to encourage participation and engagement. Friendly competition can boost morale and make learning more fun. Positivity is a great motivator.
Monitoring, Incident Response, and Recovery
Effective monitoring detects and responds to security incidents quickly. Implement tools that track network activity, system logs, and user behavior. Detection is half the battle.
Develop a documented incident response plan. This should outline the steps to take in case of a breach or attack. A plan ensures a coordinated and efficient response, cutting response time.
Regularly test and update your incident response plan. Simulate attacks and practice the response process. This helps identify weaknesses and improve the team’s readiness. Practice makes perfect.
Have a backup and recovery plan in place. This ensures you can restore your systems and data in the event of a disaster. Backup and restoration are key to business continuity.
Document lessons learned from each incident. Use this information to improve your security posture and prevent future attacks. Learning helps prevent repetition.