Imagine managing a data center where storage, compute, and networking are complex, siloed entities requiring specialized expertise and leading to inevitable bottlenecks. Sound familiar? The reality is that traditional IT infrastructure can be a real headache.
But what if you could simplify everything, collapsing these layers into a single, manageable system? That’s where hyper converged infrastructure (HCI) comes in. HCI essentially integrates these critical components into a software-defined platform, streamlining operations and boosting efficiency.
In this article, we’ll delve into the benefits of HCI, exploring how it can reduce costs, improve scalability, and enhance overall performance. Get ready to discover how HCI can revolutionize your IT infrastructure and empower your business to thrive in today’s fast-paced digital landscape.
Understanding Hyperconverged Infrastructure (HCI): A Deep Dive
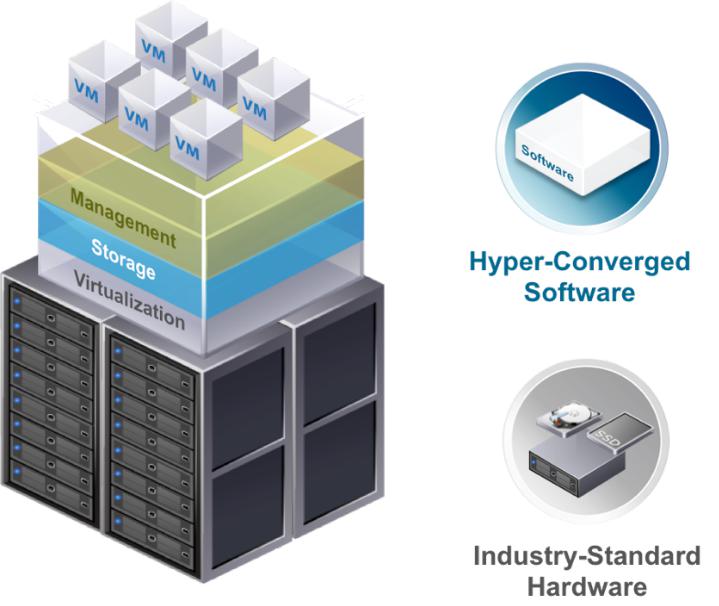
Hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) is shaking up the data center landscape. It combines compute, storage, networking, and virtualization resources into a single, integrated system. Managing IT becomes simpler and easier than before.
This architecture allows companies to sidestep intricate, legacy infrastructure. It’s all about consolidating resources. This allows organizations to focus on their core business operations and innovation, without getting bogged down by complexity.
Think of HCI as a building block approach to IT. Resources scale easily, enabling businesses to add capacity as needed. This adaptability is crucial in today’s fast-paced digital world, where demands can shift rapidly.
Moreover, HCI can make use of readily available and affordable hardware. Many vendors offer pre-integrated HCI appliances. This makes deployment a much quicker process compared to traditional IT setups.
Key Components of HCI
At its heart, HCI consists of a few crucial components working in harmony. Virtualization plays a key role. It abstracts the underlying hardware resources and distributes them to virtual machines (VMs) or containers.
Software-defined storage (SDS) pools the storage capacity of the nodes in the cluster. SDS creates a shared storage resource. This is then managed by software, offering features like snapshots, replication, and data deduplication.
Software-defined networking (SDN) manages the network traffic between VMs and containers. SDN uses software. This allows for automated network configuration, micro-segmentation, and quality of service (QoS) policies.
The management layer provides a single pane of glass for administering the entire HCI environment. This simplifies tasks such as provisioning VMs, monitoring performance, and managing storage policies for a more streamlined process.
Benefits of Adopting HCI
The advantages of HCI are numerous, enticing many organizations to make the switch. Reduced capital expenditures (CAPEX) are a major draw. This is due to the consolidation of hardware and simplified management.
Operational expenses (OPEX) also tend to decrease. HCI reduces the burden of managing complex infrastructure, freeing up IT staff to focus on other strategic initiatives. Automation is key.
Improved scalability is another significant benefit. Scaling HCI resources becomes simple. Adding more nodes to the cluster takes just a few clicks, providing agility for a fast-paced environment.
Simplified management reduces the day-to-day hassle. A unified management interface makes it easier to monitor and manage the entire infrastructure. No more juggling multiple systems or tools.
Use Cases for HCI
HCI shines across a diverse set of environments and workloads. Virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) is a prime example. HCI delivers consistent performance and simplifies management for virtual desktops.
Private cloud deployments benefit greatly from the agility and scalability of HCI. The infrastructure foundation helps facilitate self-service IT. This enables internal users to provision resources on demand.
Remote office/branch office (ROBO) environments also find HCI appealing. A centralized solution simplifies management and offers local performance. Businesses benefit from the low footprint of HCI appliances.
Business-critical applications, such as databases and ERP systems, can run efficiently on HCI. Its resilient architecture and performance optimization features ensure availability and responsiveness.
HCI vs. Traditional Infrastructure: A Comparison
Traditional infrastructure often involves separate servers, storage arrays, and networking devices. This results in complexity and silos. Managing all of these disparate components can be difficult.
In contrast, HCI consolidates these resources into a single system. This simplifies management. It offers a unified view of the entire infrastructure, improving visibility and control.
Traditional infrastructure also tends to be more rigid. Scaling resources can be a lengthy and disruptive process. HCI offers a more agile and flexible approach. Resources can be added in incremental steps.
Deploying and managing traditional infrastructure requires specialized expertise in different domains. HCI reduces the need for specialized knowledge with a single, integrated management interface. Less time spent on maintaining means more time for innovation.